How to Find Angle in Projectile Motion
Subsequently one may also ask how does the angle affect the range of a projectile. From the first equation we get t x 100 cos θ.

Proj Motion Formulas Projectile Motion Physics Lessons Physics Mechanics
You can work out the horizontal and vertical velocities at the time of impact - sketch them out head-to-tail and find the angle the resultant makes to the horizontal.

. This means θ 45 degrees. The position of the projectile as a function of time is given by x 100 t cos θ y 100 t sin θ g 2 t 2. Δ t 3s.
And this rocket is going to launch a projectile maybe its a rock of some kind with the velocity of ten meters per second. The equation for the distance traveled by a projectile being affected by gravity is sin 2θv2g where θ is the angle v is the initial velocity and g is acceleration due to gravity. As we discussed previously T T depends on the initial velocity magnitude and the angle of the projectile.
Yes - its the arctan. 2 ms 30 vH vv 1 ms 173 ms make sure you are in degree mode R évsin. The time of flight of a projectile motion is the time from when the object is projected to the time it reaches the surface.
Xvxtxvxt where vxvx is the x-component of the velocity which is given by. Time t for both motions is the same so x is. Horizontal motion is a constant velocity in the absence of air resistance.
2 - Projectile Motion Calculator and Solver Given Range Initial Velocity and Height Enter the range in meters the initial velocity V 0 in meters per second and the initial height y 0 in meters as positive real numbers and press Calculate. P that defines the projectiles height as a function of horizontal distance x. Recalling that 1 cos 2 θ 1 tan 2.
R Û L 2 866. The trick is to split the velocity into horizontal and vertical components. V yo 30 ms.
The goal is to eliminate the initial unknown velocities where v x v i cos θ v y v i sin θ To do this we use equations x v i cos θ t. This projectile calculator makes your task easier as you dont have to perform manual calculations with projectile motion equations to find the values for projectile motion. V y V yo sin 70 V y 30 sin 70.
If α 90 then its a freefall. Ux 60cos30o u x 60 cos 30 o. Thus v x v ᐧ cos𝛳2 Where 𝛳2 30 and v is velocity when an object makes angle 𝛳 30 with the horizon.
For this calculator you need to know the 3 required values so you can enter them in the spaces provided. We can first find the angle since the initial and final velocities are not given while the initial displacement are given as X Y 0 and the final displacement as X 457 m and Y 061 m. Construct a right-angled triangle from vectors.
V y 2322 ms. The first parabola would be s 40t 981t22 and the second parabola would be s 40 t - 2 981 t - 222. The vertical velocity in the y-direction is expressed as.
3 We now have one equation that describes the motion of the projectile which is useful in. The maximum height of projectile is given by the formula. The formula to find the angle is where v is initial launch speed g is the gravity constant x and y are the targets distance and height.
- Horizontal velocity Vx V x cos α - Vertical velocity Vy V x sin α - Three vectors V Vx and Vy a right triangle If the vertical velocity is zero then you have horizontal projectile motion. Uy 60sin30o u y 60 sin 30 o. Then enter the value of the Angle of Launch and choose the.
The Equation of Trajectory. As it rises and falls air resistance has a negligible effectThe distance traveled horizontally from the launch position to the landing position is known as the rangeThe range of an angled-launch projectile depends upon the launch speed and the launch angle angle between the launch direction and. R é L 2sin 30 R Û L 2cos 30 R é L25.
The outputs are the initial angle needed to produce the range desired the maximum height the time of flight the range and the equation of the. Let θ be the firing angle. See the video below to understand projectile motion in a better way.
Here in the first case the angle of projection is 60 and initial velocity u 10 ms. - Voiceover So Ive got a rocket here. Find its initial horizontal and vertical velocities.
And the direction of that velocity is going to be be 30 degrees 30 degrees upwards from the horizontal. Now the vertical component of velocity v y changes during motion but v x remains constant. The two roots of this equation give you two possible angles.
A projectile is launched at 60 ms-1 at an elevation of 300. To calculate projectile motion without an angle we have to know the equations of motion which are. Find the horizontal and vertical velocity components.
If Jhonson tosses a ball with a velocity 30 ms and at the angle of 70 then at the time 3s what height will the ball reach. Or the angle between the direction of the launch and. Solving for t in 1 and substituting into 2 yields t x vcos and therefore pxhvsin x vcos 1 2 g x vcos 2 hxtan gx2 2v2 sec2.
Assuming that v 2 g is constant the greatest distance will be when sin 2θ is at its maximum which is when 2θ 90 degrees. T 2uy g T 2usinθ g T 2 u y g T 2 u sin θ g Acceleration. Thus v x u ᐧ cos60 10 x 05 5 ms.
An object is kicked at a velocity of 2 ms at an angle of 30. Of a projectile fired at an angle at h0 with initia. Letting x 10 and substituting into the equation for y one obtains 2 50 10 tan θ g 200 cos 2 θ.
Establish the equations of motion. In these equations v is the final velocity measured in metres per second ms u is the initial velocity measured in ms a is the acceleration measured in metres per second squared ms 2 s is the displacement measured in metres m and t is the time measured in seconds s. The equations would be based on s ut at22 where s is the height u is the initial velocity t is the time elapsed and a is the acceleration due to gravity.
If v is the initial velocity g acceleration due to gravity and H maximum height in meters θ angle of the initial velocity from the horizontal plane radians or degrees.

Mathematics Encyclopedia Projectile Motion Part 2 Projectile Motion Motion Physics Geometry Sheets

Math Principles Projectile Motion Problems Projectile Motion Motion Problem

Proj Motion Formulas Projectile Motion Physics Mechanics Physics

Projectile Motion Physics Problems Projectile Motion Physics And Mathematics

Speedy Drives Off A Cliff Projectile Motion Problem Video Physics Projectile Motion Motion Physics

Projectile Motion Question Using Kinetic And Potential Energy Physics Classroom Physics And Mathematics Projectile Motion

Resultat De Recherche D Images Pour Long Jump Take Off College Physics Physics Physics Concepts

Physics 2d Kinematics Projection Motion Horizontal Launch Physics And Mathematics Physics Physics Lessons

Projectile Motion Of A Particle Projectile Motion Physics Formulas Physics Mechanics
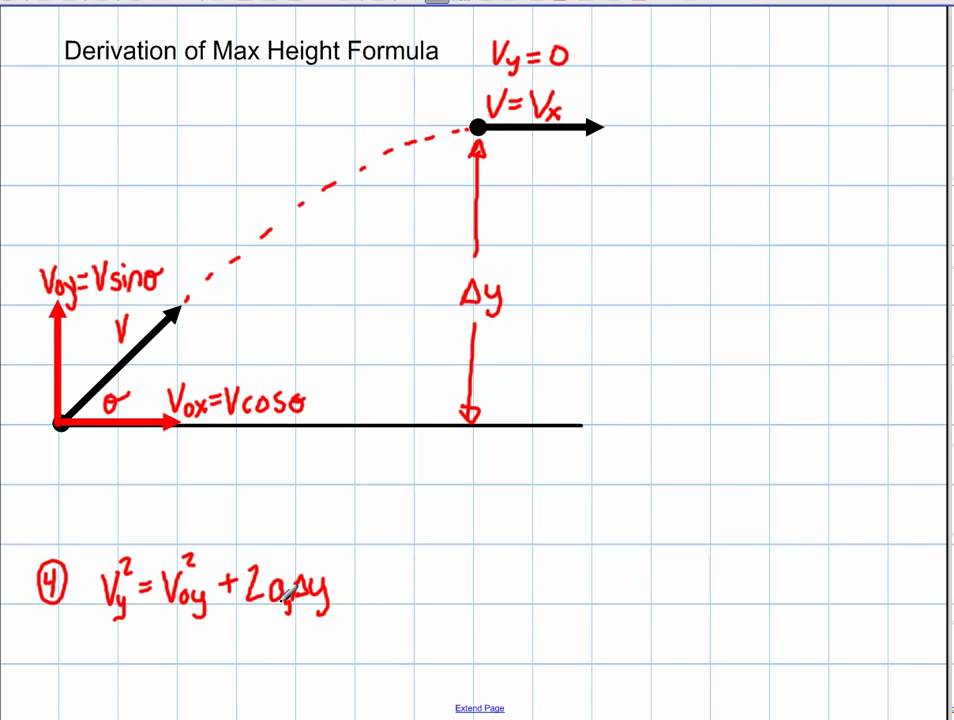
Physics 2d Kinematics Deriving Max Height Of A Projectile Physics Studying Math Physics Formulas

Projectile Motion Physics Mechanics Quadratics Physics

Check It Out Equations Solving Technology

2 D Projectile Motion Explained Youtube Ap Physics Motion Physics Physics

Projectile Motion Example Problem Physics Homework Help Science Notes And Projects Projectile Motion Learn Physics Physics

Projectile Motion Projectile Motion Simulation Projectile Motion Best Airplane Games Flight Simulator

Vertical Velocity Calculator Velocity Physics Calculator

Projectile Motion Projectile Motion Motion Wikipedia

Question 3 9 Chapter Three Motion And Force Chapter Force Motion

Projectile Motion Of A Tennis Ball Teaching Resources Projectile Motion Tennis Ball Engineering Science
Comments
Post a Comment